|
|
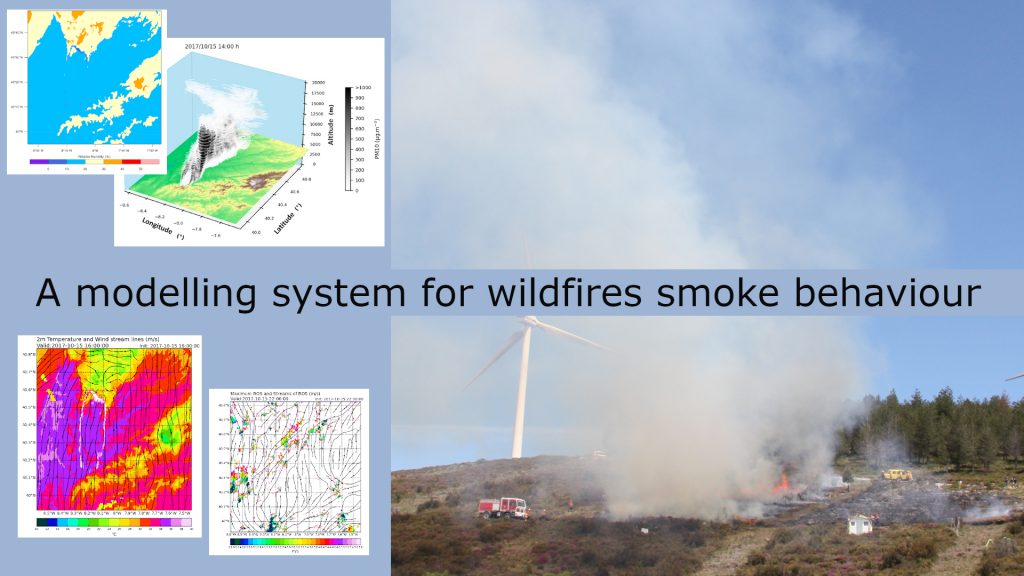
ABOUT FIRESMOKEThe FIRESMOKE project aims to enhance the weather forecast model BRAMS, which internally couples an air chemistry model (CCATT) and a surface forest fire propagation model (SFIRE), enabling short-term and real-time simulations. Within the project’s scope, further advancements in the BRAMS model will be undertaken, particularly in the surface wildland fire propagation model (SFIRE). This enhancement will incorporate crown tree fire propagation, and the resulting smoke from both the surface and tree canopy will be introduced into the Eulerian Coupled Chemistry, Aerosol, and Tracer Transport model (CCATT). |
OBJECTIVES1) The goal is to obtain real-time estimates of fire plume behavior, not only derived from surface forest fires but also including fires originating in canopy trees. This aims to simulate fires in areas with complex forest fuel, creating an integrated fire forecasting system. This system can monitor air quality and pollutant dispersion trajectories from these smokes, and simultaneously simulate anthropogenic and biogenic pollutants. |
 |
 |